Free shipping on all orders over $50 | Subscribe & save 15%
Free shipping on all orders over $50 | Subscribe & save 15%

Using calcium glycerophosphate for Interstitial Cystitis, or Bladder Pain Syndrome (IC/BPS), isn’t a new concept. Many people have been privy to the benefits of this compound in helping with the symptoms of IC/BPS.
IC/BPS is a chronic condition that affects millions of people (primarily women) worldwide. It disrupts the regular functions of the bladder and can cause tremendous pain in the surrounding pelvic area. This condition can be challenging and debilitating. It has many symptoms, like needing to pee urgently, pain in the pelvis, and having to pee often at night.
In this article, we’ll look at the advantages of using calcium glycerophosphate in the management of IC/BPS.
Listen to Femetry’s own Dr. Jennifer Anger discuss the many benefits of calcium glycerophosphate.
There is currently no cure for IC/BPS. Moreover, IC/BPS is difficult to treat and diagnose because of its unique nature. Treatment options are geared towards alleviating the symptoms to make life more bearable for the patient.
Unfortunately, symptoms tend to vary in occurrence and severity for each patient, making it a struggle to manage. For someone with IC/BPS, every day is a constant battle inside your body.
There is much to learn about IC/BPS, but this allows for innovation, inspiration, and endless treatment possibilities. Doctors and patients collaborate to make treatment plans with lifestyle changes, medications, bladder instillations, and supplements. Learn more about useful supplements for IC.
Still, many IC/BPS patients continue to search for more effective solutions to improve their quality of life. Let’s explore calcium glycerophosphate.
Calcium glycerophosphate can be great for your teeth. It is known to offer bone support.

Calcium glycerophosphate is a compound that combines calcium and glycerophosphoric acid. You might be familiar with it from certain kinds of toothpastes and other dental products that help prevent cavities. We’ll take a look at the other ways this compound could be useful if you have IC/BPS.
In the context of IC/BPS, calcium glycerophosphate helps to neutralize acids. Food or beverages that contain a high level of acid can trigger an IC flare for many people. For this reason, taking an antacid could help mitigate the effects after consuming a known dietary trigger.
That’s where calcium glycerophosphate comes in with its alkalizing effect on urine. It is often combined with sodium bicarbonate to create a powerful compound that helps neutralize acids, and subsequently, improve symptoms.
By increasing the pH level of urine, calcium glycerophosphate helps foster a less acidic environment in the bladder. This shift can be particularly beneficial for people with IC/BPS. Often, acidic urine can worsen symptoms and contribute to bladder irritation. Surveys have shown a 20-30% reduction in symptoms when IC/BPS patients consume alcohol, chocolate, and carbonated drinks.
The cause of IC/BPS is still unknown. One theory suggests that patients may have more oxalates in their urine. Oxalates are natural compounds that are present in many fruits and vegetables. If your body has too many, however, it could result in the formation of crystals, or kidney stones.
Kidney stones can travel to the bladder, damaging the bladder walls or in general aggravating IC/BPS symptoms. Research shows that rising pH levels create an environment that inhibits oxalate crystallization.
Since calcium glycerophosphate has an effect on pH, the theory is that it could help to decrease the presence of these crystals. This would impact the frequency and intensity of a flare for IC/BPS patients. Keep in mind, this is a hypothesis and still requires more research to determine efficacy.
Another theory about the underlying cause of IC/BPS is inflammation. Doctors are unsure of which comes first, the IC/BPS or the inflammation. But one thing is certain: chronic inflammation is a hallmark of IC/BPS.
Calcium glycerophosphate emerges as a promising ally. It can play a pivotal role in mitigating the inflammatory response within the bladder. By supporting your body’s inflammatory response, this compound may unlock relief from pain and promote overall bladder function.
When you have IC/BPS, there’s a lot of trial and error to discover what works for you. Calcium glycerophosphate could be a powerful companion to add into your daily routine. It helps balance pH levels and has special qualities that can be life-changing for people with IC/BPS.
For more information about our potent ingredients, visit our Ingredient Glossary.
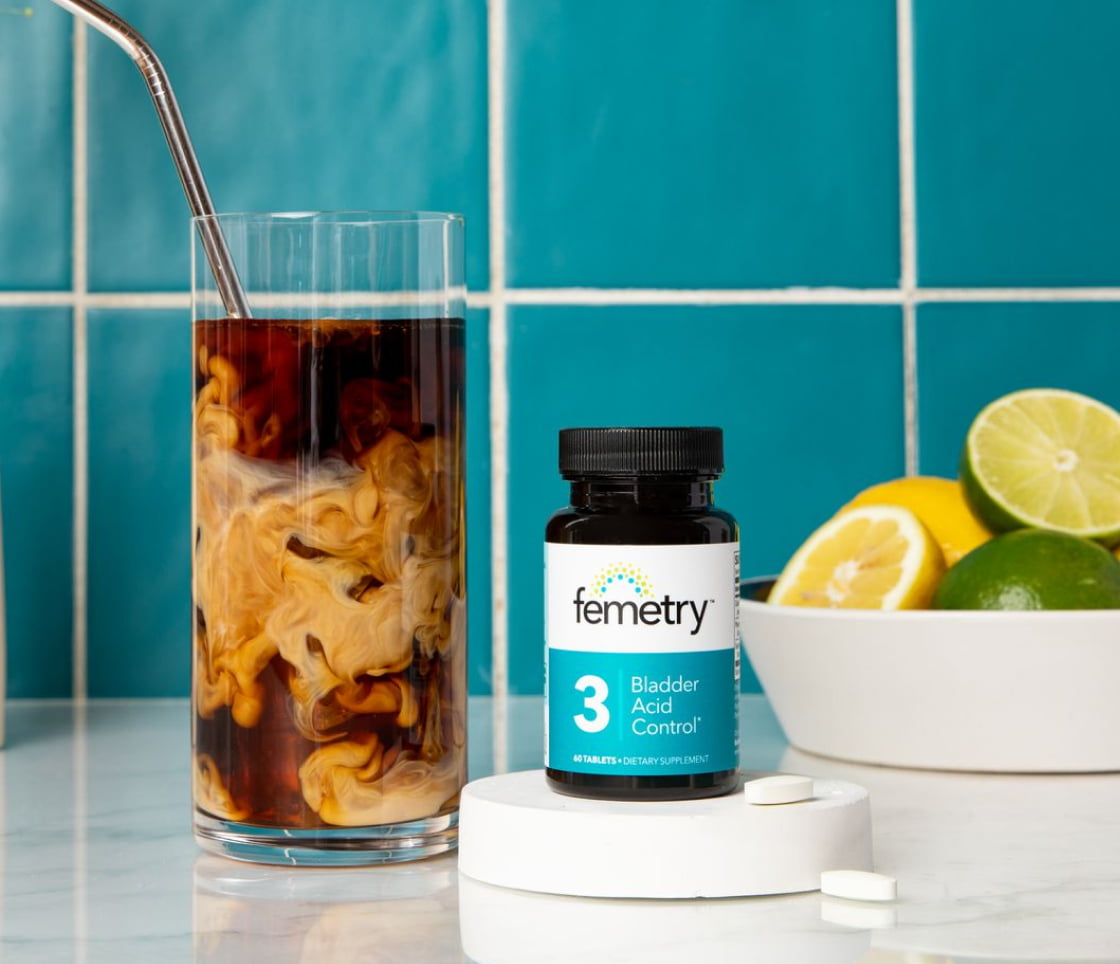

Bladder Acid Control contains 50% more calcium glycerophosphate per tablet than another leading brand, plus the addition of sodium bicarbonate. That means you get more acid-reducing power (and can perhaps take less tablets) to achieve the desired effectiveness.
Learn more